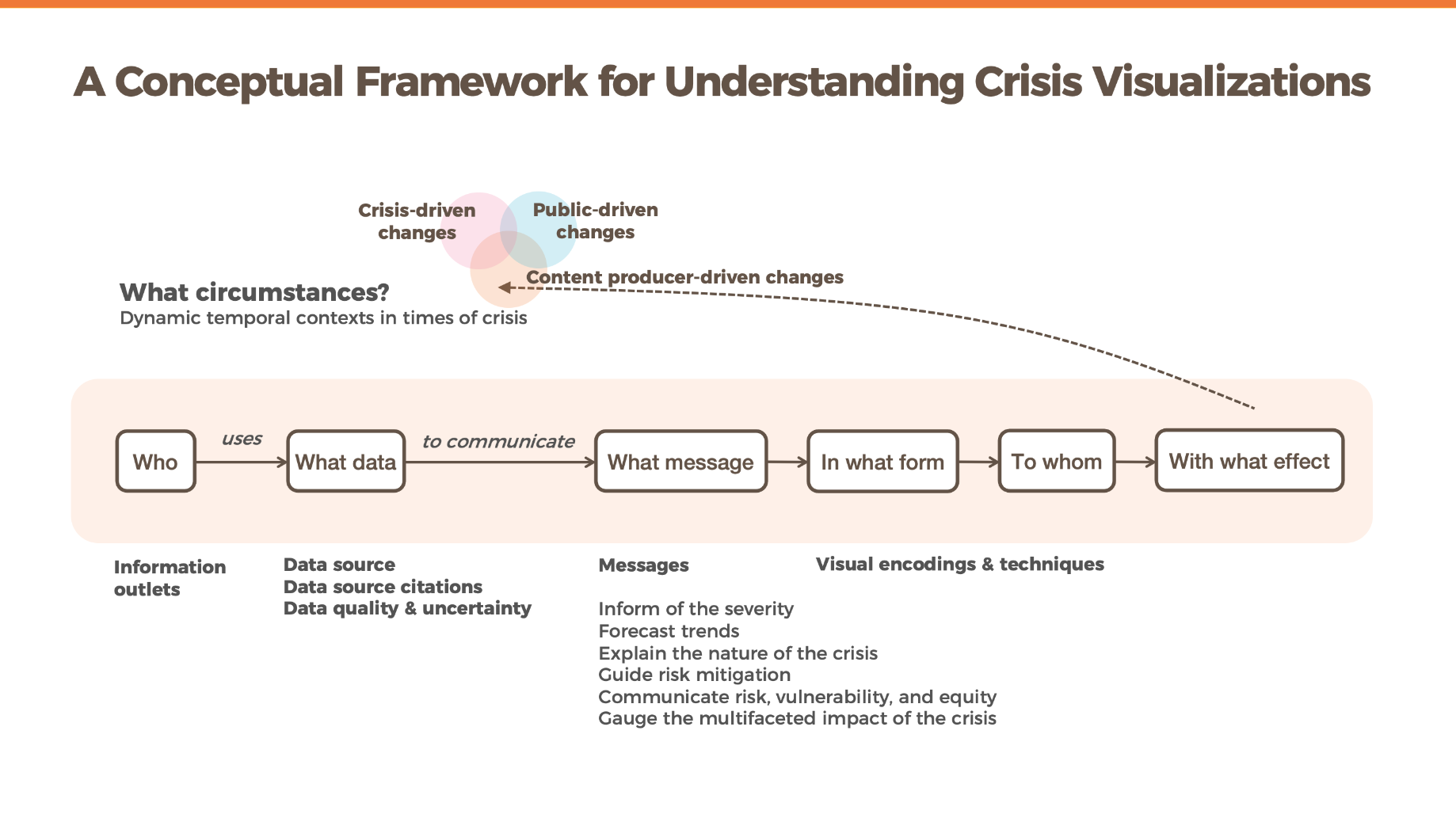
In response to COVID-19, a vast number of visualizations have been created to communicate information to the public. Information exposure in a public health crisis can impact people's attitudes towards and responses to the crisis and risks, and ultimately the trajectory of a pandemic. As such, there is a need for work that documents, organizes, and investigates what COVID-19 visualizations have been presented to the public. We address this gap through an analysis of 668 COVID-19 visualizations. We present our findings through a conceptual framework derived from our analysis, that examines who, (uses) what data, (to communicate) what messages, in what form, under what circumstances in the context of COVID-19 crisis visualizations. We provide a set of factors to be considered within each component of the framework. We conclude with directions for future crisis visualization research.
Our research group examines how novel interactive computing systems can help people to achieve a state of wellness, as defined by the World Health Organization: "Wellness is the realisation of the fullest potential of an individual physically, psychologically, socially, spiritually and economically."
We are particularly interested in issues of health equity, designing innovative software tools for populations who disproportionately experience barriers to wellness. To this end, our research explores how social, mobile, and ubiquitous software systems can support health literacy, healthy behaviors, and health advocacy in low-socioeconomic and racial/ethnic minority groups. The Wellness Technology Lab utilizes user-centered, participatory design methods to design and build engaging and motivating software systems, and conducts in-depth field studies to evaluate user experience with and impact of these tools. Our work contributes to the fields of human-computer interaction (HCI), computer-supported cooperative work (CSCW), social computing, ubiquitous computing (Ubicomp), and personal/consumer health informatics.