2015-16 Research and Engagement Grants
Applying Design Studio Pedagogy in STEM Learning with Novel Presentation and Sensing Technologies
Betsy DiSalvo, Mark Guzdial, Blair MacIntyre
(Supported by GVU and IPaT)
This project takes the open collaboration teaching methods of design studios and uses them in STEM learning, with the goal of creating more motivation to learn.
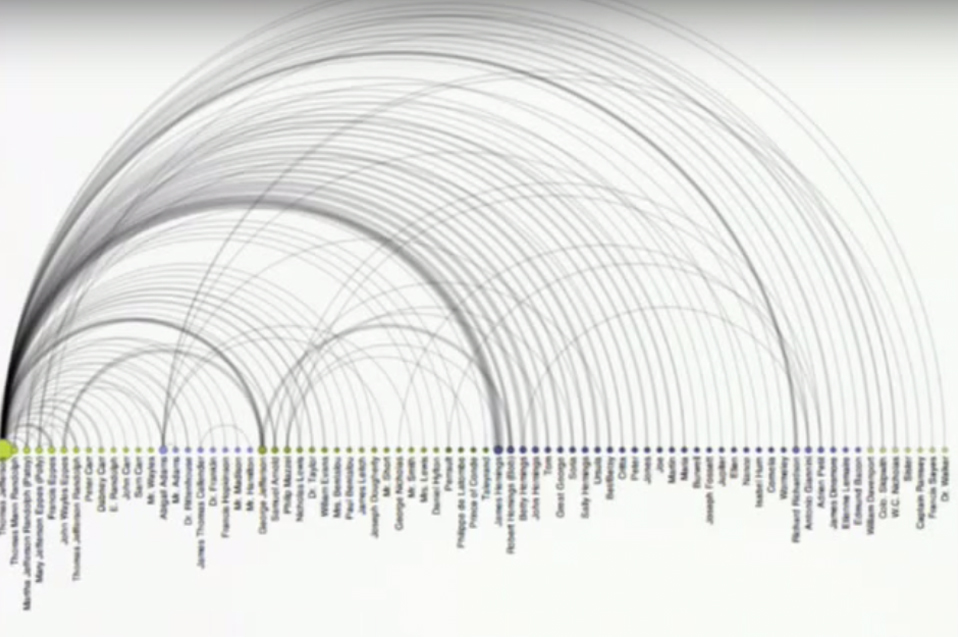
Reimagining Humanities Visualization: A Research-Through-Design Workshop for Civic and Cultural Data
Rahul Basole, Polo Chau, Carl DiSalvo, Alex Endert, Jim Foley, Nassim JafariNaimi, Lauren Klein, Yanni Loukissas, John Stasko, and Jimeng Sun
(Supported by GVU and IPaT)
Georgia Tech researchers are studying how they can use visualization techniques to explore “messy” humanistic data such as civic and cultural data. They plan to host a workshop in March 2016 for leading humanities scholars and information visualization researchers to explore the meanings of civic and cultural “data,” and to prototype new methods for their visual display. The goal is to imagine new forms and platforms capable of portraying the humanistic dimensions of civic and cultural data, and to establish Georgia Tech as a leading center of interdisciplinary visualization research.
Promoting Cognitive Systems Research at Georgia Tech

Ashok Goel, Elizabeth Whitaker
(Supported by GVU, IPaT, and GTRI)
The recent advent of famous cognitive systems such as Apple's Siri and IBM's Watson has ushered a new era in the development of artificial intelligence. Cognitive systems are intelligent systems characterized by human-level, human-centered and human-like intelligence. We seek to foster internal collaboration and enhance external visibility in cognitive systems with the goal of establishing an interdisciplinary Center for Cognitive Systems. In particular, we will organize a seminar series on cognitive systems with distinguished external speakers, monthly meetings of the internal cognitive systems faculty and staff, and yearly workshops of the local cognitive systems community including research students. In addition to the two PIs, the proposal also includes Timothy Boone, Michael Hoffmann, Margaret Loper, Julie Linsey, Keith McGreggor, Janet Murray, Amy Pritchett, Mark Riedl, Eric Schumacher, and Alan Wagner, indicating both the deeply interdisciplinary nature of cognitive systems research and broad support across the institute.
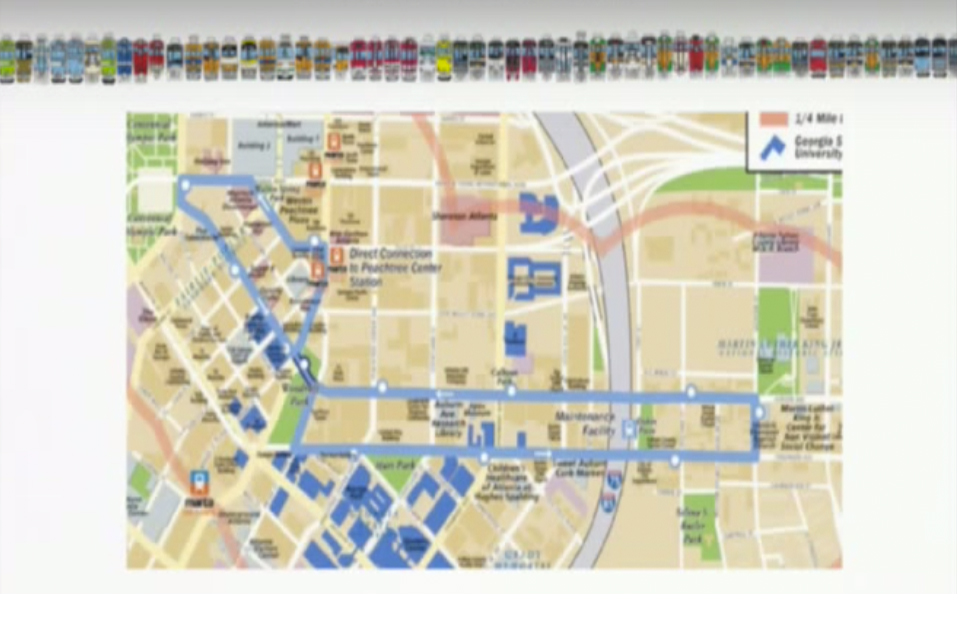
Real-Time Control to Replace Schedules on the Atlanta Streetcar
Kari Watkins, Russ Clark
(Supported by GVU, IPaT, and the Center for Urban Innovation)
Almost all public transportation in the US runs on a schedule, but schedule-based service may not be the most effective way to control operations. When transit routes are very frequent, passengers tend to arrive at stations randomly and typically disregard the schedule. Maintaining a schedule, however, requires long buffer time that wastes passengers' time and agencies' resources. To avoid the need for schedules while maintaining stable operations, we have developed a bus dispatching system that uses real-time information to maintain even spacing between transit vehicles. In partnership with GVU Center, IPAT, Center for Urban Innovation, and City of Atlanta, we will test this control method on the Atlanta Streetcar using tablets inside the streetcars to communicate driving instructions to the operators. The objective will be to maximize the quality of service only using available resources. The implementation has the potential to drastically reduce passenger waiting time on the Streetcar corridor, and later on other transit routes in Atlanta, and throughout the country.
2014 Research and Engagement Grants
VIDEO: Project overviews at Brown Bag Replay (18 minute mark)
Digital Policy: Communication Tools to Shrink the Science to Policy Gap
Autism prevalence rates in the United States have more than doubled since 2000 (from 1 in 150 to 1 in 68 children being identified). Despite this trend as the nation's fastest growing developmental disability, many insurance providers, including Medicaid, do not cover autism services or early intervention services for
Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD). ASD affects all races, ethnicities, and cultures, as well as broadly across the socioeconomic spectrum. Empirical evidence has shown that the costs of late or undiagnosed ASD is 320% more than early diagnosis and behavioral therapy. The current $60 billion cost of treatment for ASD is expected to grow to $200-‐400 billion in a decade, if current treatment trends continue (based on previous prevalence rates of 1 in 88 children). In addition to the economic savings of early intervention treatment, benefits to funding early intervention include decreased family burden and workplace absenteeism for caregivers, increased economic and social outcomes for patients, and reduced burden on already overtaxed social service systems for adults.
Our research project draws on policy research and human-‐centered design research to build communication tools (“digital boundary objects”) that aid the public and legislators in understanding the negative economic impact of late intervention and providing an evidence base for the justification of passage and implementation of early intervention services in ASD. The first set of communication tools is aimed at policymakers to improve the continuum of care and interagency system of supports for children with autism. We foresee variations of these tools to be used by the public for raising awareness and enabling collective action.
Nassim JafariNaimi, School of Literature, Media, and Communication
Kim Isett, School of Public Policy
Exploring Movement-‐based Games to Encourage Social Behaviors in Children with Autism
This project aims to identify effective feedback mechanisms for encouraging collaboration and social interaction among children with autism in motion-based games.
Our focus is motivated by decades of research suggesting that individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) experience specific difficulties with peer interactions and friendships. Such interactions and relationships play a critical role in social learning throughout the lifespan, and are a frequent target of behavioral interventions. A growing body of research suggests that games may be a particularly effective mechanism for social skills training in ASD. One key advantage of using games or virtual environments to target these skills is the simplified and predictable nature of the interactions enabled by these technologies. Individuals with ASD may find the multi-sensory nature of social interactions overwhelming, so interactions mediated with and through technologies may represent a powerful stepping-stone to practicing and building social skills. We focus on motion-based (kinect) games because inhabiting a virtual space with a peer may be a particularly effective approach for scaffolding social interactions for individuals with ASD, and targeting additional skills of particular relevance such as self- and other-awareness and motor coordination.
Agata Rozga, School of Interactive Computing
Brian Magerko, School of Literature, Media, and Communication
Ashley Cheek, The Lionheart School
Victoria McBride, The Lionheart School
The Move Lab: A STEAM Community of Learners
Contemporary art centers are changing, moving beyond delivery of content to embrace participatory art and learning models. Part of this move involves engaging audiences more frequently with technology, both as participants via technology, and producers of content that is enabled by technology. However, we do not have a full understanding of what this model can look like nor how to evaluate learning within it. To better understand these models of participation with STEAM (Science Technology Engineering Art and Math), the Georgia Tech Culture and Technology Lab (CaT Lab), in collaboration with Eyedrum, propose the Move Lab project. The Move Lab will invite participants, including working artists, technology experts, undergraduates, and high school students, to work together for a full week to produce a multimedia dance and technology performance speaking to issues of technology and culture. Our goal is to use the Move Lab as a model for future collaborations between artist and technologist, and as a case study to better understand the aspects of transformation in participation identified by Rogoff [8] as central to the evaluation of individual learning and development with STEAM.
Betsy DiSalvo, School of Interactive Computing
Al Matthews, Eyedrum
Onar Topal-Sumer, Eyedrum
Patients' Information Needs Related to Diagnostic Processes around Health Concerns
This project outlines collaborative research between the School of Interactive Computing at Georgia Tech and Diagnostic Radiology
at Emory Healthcare, to develop methods for capturing and analyzing patients' information needs related to diagnostic processes around health concerns. Our research will utilize large-scale activity manifested in a variety of online health information resources, targeting social resources like Facebook, Twitter, and reddit. We will complement this approach and validate the quantitative findings relating to patients' needs with surveys and field-based interview methods. The qualitative approach will pursue first-person accounts of the information needs of Emory Healthcare patients as they are both reported by patients and expressed in patient-clinician consultations.
The insights resulting from this research will:
• Inform the design of novel online social tools. The research outlined in this seed grant proposal will yield both design guidelines and software specifications necessary to develop tools to better serve patients' information needs related to diagnostic testing. We anticipate that such tools will enable people to more easily share and access information from other individuals experiencing similar health concerns, and/or navigating their own diagnostic processes.
• Provide the preliminary data upon which a larger collaborative grant proposal will be based. Data captured from the research
outlined here will guide a larger future collaborative grant proposal involving Emory Healthcare and Georgia Tech.
Lauren Wilcox, School of Interactive Computing
Munmun De Choudhury, School of Interactive Computing
Aarti Sekhar, Emory Healthcare
Wearable Technology Exhibition Digital and Literary Extension
The Georgia Tech-curated exhibit “Meeting the Challenge: The Path Towards a Consumer Wearable Computer” made its debut at CHI 2014 with more than 1,000 visitors to the exhibition. The wearable technology showcase subsequently went on to two locations in Germany and at a World Economic Forum meeting in China. The exhibit will make its campus debut in October 2014. Curators of the exhibit have started to develop an online version of the exhibition athttp://wcc.gatech.edu and propose extending this online exhibition and revamping its interface. It will be a jumping off place for companies to become more involved with the GVU Center research community and also allow students to use the website as a source for project inspiration. This online exhibition can also be formatted to work on a large touch screen surface.
A companion print piece of the exhibition will create a narrative of the showcased technology, telling a more detailed story of the history of wearable computing. This book will be a lasting legacy of the exhibition and a record of the research and innovation in the wearable technology field and at Georgia Tech. An e-book version will have videos of the exhibition's creation, along with archived interviews and videos of wearable computers in use. The e-book can also have links to referenced academic papers and consumer products. This piece will also augment visitors' experiences to the physical exhibition.
The digital and literary extension project will recognize the many areas of study for wearable computers, including opportunities in computer science, industrial design, and even psychology as researchers consider user studies and computing on the body.
Clint Zeagler, School of Industrial Design
2013 Research and Engagement Grants
VIDEO: Research Project Overviews (GVU Brown Bag, August 2013)
Implementation and Assessment of One-Bus Away Atlanta
Transit provides mobility to those who cannot or prefer not to drive, including access to jobs, education and medical services. Transit reduces congestion, gasoline consumption and the nation's carbon footprint. However, from a customer perspective, a mobility choice is only a choice if it is fast, comfortable and reliable. One inexpensive way to combat unreliability from the user perspective is real-time transit information. The OneBusAway transit traveler information system was originally developed at the University of Washington by Dr. Brian Ferris, Dr. Kari Watkins, and Dr. Alan Borning to provide real-time bus arrival information for riders in greater Seattle-Tacoma. OneBusAway is comprised of multiple interfaces to access information, including a website, a telephone number, text-messaging, a mobile-optimized website, and native applications for both the iPhone and Android platforms (see http://onebusaway.org); it currently hosts more than 100,000 unique users per week. OneBusAway was developed under multiple federal grants as an open-source system allowing other transit agencies to adapt the code for their own systems. Additional deployments using the code base have begun in New York City, Tampa and now Atlanta. Previous studies have shown that real-time can increase transit ridership, increase satisfaction with transit performance, improve perception of safety, and decrease perceived and actual wait time. The goal of the Atlanta deployment is to provide a service to area transit riders and to further quantify the impacts of real-time information by conducting a study of OneBusAway users and compare their ridership and perceptions to those of non-users.
Team: Kari Watkins, School of Civic and Environmental Engineering; Russ Clark, School of Computer Science
Launch Support for The Game Studio at Georgia Tech
The Georgia Tech Game Studio is a new, internal, by-application game design and development organization focused on facilitating the creation of novel, excellent, complete games. The Studio aims to increase the Institute's reputation in the production of original games, both through commercial success and participation in competitions and festivals. The Studio will help participants conceptualize, design, develop, and release original games by providing space, materials, and industry advisement.
Team: Ian Bogost, School of Literature, Media & Communication; Blair MacIntyre, School of Interactive Computing
Computational Social Science Workshop and Hackathon with Emory
The emerging cross-disciplinary field of computational social science is transforming both research and industry by combining computational methods with social science theory and research. GVU has a unique capability to shape this emerging discipline, building on the center's tradition of interdisciplinary research. To add a strong social science foundation, GVU will team with researchers at Emory University to offer two community-building activities for Computational Social Science in 2013-2014. In the fall, we will offer a Research Workshop featuring distinguished visiting speakers and presentations from GVU and Emory faculty; in the spring, we will reconvene for a freewheeling Hackathon that brings students and faculty together to form interdisciplinary research teams working on projects of mutual interest.
Team: Jacob Eisenstein, School of Interactive Computing, Eric Gilbert, School of Interactive Computing + collaborators at Emory University
FIDO - Facilitating Interactions for Dogs with Occupations
Working dogs, whether assistance, medical, or military dogs, have important information to impart to their human handlers. However, communication between human and canine partners is currently limited. Handlers give verbal or hand signal commands, and dogs respond with trained behaviors such as alerting with a paw or nose touch, or barking. Improving dog-to-handler communication could literally save lives. A medical alert dog could directly summon aid. If a hearing dog could tell his handler specifically whether the source of the sound was the phone ringing or the fire alarm, the handler could make better decisions about how to respond. Military dogs could mark bomb locations and even indicate the type of bomb found, then move to safety, rather than the current practice of lying next to the bomb and barking until the handler arrives, putting both dog and handler at risk. Silent handler-to-dog communication could be critical as well, as voice and hand signals make dog handlers targets for snipers. Improving communication through technology could have profound implications for working dog teams in many domains. We plan to leverage Georgia Tech's extensive experience in wearable computing to enable communication with animals. We have created the Inter-species Interaction Lab to establish Georgia Tech as a pioneer in the little-explored space of Animal-Computer Interaction, studying communication with animals mediated by technology.
Team: Melody Moore Jackson, School of Interactive Computing, Thad Starner, School of Interactive Computing, Clint Zeagler, School of Industrial Design
Games@GaTech
Games @ Gatech is an institute-wide initiative to leverage Georgia Tech's leadership role in video games research and education by aggregating and incubating interdisciplinary games research and academic activities across the campus. This goal of this initiative is twofold: First, to bring together diverse games activities and foster greater internal awareness, research collaboration, and funding access among entities and individuals with the institute; second, to help create a single, more focused Georgia Tech "brand" to the outside world that improves public awareness of the institute's collective strengths in game-related research. Games @ Gatech will help create a more unified research community, advancing interdisciplinary research, and facilitating better exposure to funding opportunities, tech transfer and industry partnerships.
Team: Celia Pearce, School of Literature, Media & Communication; Mark Riedl, School of Interactive Computing
Sonic Generator and the National Orchestra of Lorraine
Sonic Generator, the high-tech contemporary music ensemble in residence at Georgia Tech, joins forces with members of L'Orchestre National de Lorraine and their conductor Jacques Mercier to present concerts at the Ferst Center for the Arts at Georgia Tech (November 3rd, 2013) and at L'Arsenal in Metz (February 15, 2014). The performances will feature innovative French and American contemporary music including Steve Reich's City Life, a new commission from Daniel Wohl, and music by GT professor Jason Freeman. These concerts will help celebrate the fifth edition of France-Atlanta and the twenty-fifth anniversary of L'Arsenal and initiate new conversations about the role of the arts at Georgia Tech's Lorraine campus.
Jason Freeman, School of Music.edu/plugins/shows/index.php?id=556
Simulating Activities of Daily Living: Dressing Clothes (Supported by GVU, IPaT, and RIM)
Dressing clothing is considered as one of the Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) for an individual to maintain a functional life independently. Unlike other ADLs, such as feeding and mobility, dressing is unique to human society and is one of the most important milestones of self-care development for a child. An average child takes 24 months to develop sufficient coordination and manipulation skills to put on loose clothing. It will take another year or two before she will be able to get dressed all by herself. This is mainly due to the combined difficulty in coordinating different body parts and manipulating soft and deformable objects (clothes). This project aims to recreate this unique human behavior through physical simulation and eventually enables assistive robots to dress real humans. In particular, we are interested in designing motor control algorithms for dressing upper and lower body for oneself and others. Beyond robotic applications, we expect to expand the current biomechanical knowledge in human coordination control mechanism, to advance the control algorithms for high-dimensional, nonlinear systems in control theory, and to enhance the state-or-art simulation techniques for manipulating deformable objects.
Karen Liu, School of Interactive Computing
2012 Research and Engagement Grants
Computational Play
We currently have little understanding of how people and intelligent agents might engage in unstructured, co-creative domains, where each team member takes an equal part in applying creative problem solving within a social context. In this project, we will investigate the problem of co-creative intelligence in the domain of imaginary play. Imaginary play is a fundamental aspect of human existence. Specifically, we will target play between humans and robotic systems, focusing on those aspects of human-robot interaction that we believe are missing in current robotics research: robot as peer to the human instead of subservient, interactivity, open-ended tasks, and evolving social roles.
Team: Brian Magerko (LMC), Andrea Thomaz (IC), and Mark Riedl (IC)
DMITRI Data Analysis
The DMITRI project has built a unique, comprehensive data set capturing daily life and diabetes management information from adult diabetics. This data includes personal logs, nutritional logs, clinical history, questionnaire data, and data from a range of on-body monitoring equipment including insulin pump dosage logs, Dexcom continuous clucose minitor, SenseWear activity monitor with accelerometer, GSR, and skin temperature sensing, Polar heart monitor, Philips Actiwatch, and Zeo sleep monitor. In this project, we aim to address the "capture and access" challenges of analyzing this data by applying our expertise in pattern recognition and wearable sensing to identify correlations and patterns in the dataset, shedding light on the impact of personal behavior on diabetes management.
Team: Thad Starner (IC) and Nate Heintzman (Biomedical Informatics, UCSD Dept. of Medicine)
Georgia Tech Campus Driving Simulation and Research
Applying driving simulators for in-vehicle research allows for a wide range of studies to be performed particularly when investigating cognitive demand and distraction caused by devices in the car. By using simulations, researchers can investigate driving behaviors in high-risk situations without putting participants or others in harm's way. Currently being conducted within the School of Psychology at Georgia Tech, in-vehicle research could provide more insight into behavior and increase in applicability if participants were able to drive in areas that they are familiar with. Specifically, research being done in coordination with the Atlanta Shepherd Center investigating the use of in-vehicle technologies to assist individuals who have had a Traumatic Brain Injury could benefit largely through these real location maps. The Georgia Tech School of Architecture coincidentally has already developed a 3D model of the Georgia Tech campus and some of the surrounding areas including the Peachtree corridor (26 miles along Peachtree Street). However, in order to make this model usable within the simulator, it must be optimized and converted in a compatible format. Researchers in the School of Architecture and School of Psychology will be working on creating methods and conversion processes that will allow any 3D model to be integrated into the simulator. Development of this process of conversion will allow Georgia Tech to offer documentation and map-creation services to other researchers around the world assisting in increasing the applicability of in-vehicle research.
Team: Bruce Walker (Psych/IC) and Racel Williams (Architecture)
Cycle Atlanta Crowd-sourced Bike Route Desirability
Fifty percent of all trips are 3 miles or less, yet only 1.8% of those trips are biked. Meanwhile, 35.7% of US adults are obese and the transportation sector accounts for 32% of US greenhouse gases. One of the main reasons citizens do not use the healthier mode of cycling is due to a lack of safe infrastructure-dedicated bicycle routes, roads with bicycle lanes, and other designated bicycle facilities. The City of Atlanta has a desire to put proper cycling infrastructure in place but needs better information from citizens about where they currently and would like to cycle. Therefore, the initial goal of the Crowd-sourced Bicycle Route Desirability project is to modify the open-source CycleTracks application (previously adopted in San Francisco, CA, and Austin, TX.) for use in Atlanta. CycleTracks tracks the existing routes of cyclists using their smart phones and allows comparison of these routes to the quickest path from origin to destination. This allows us to begin to make appropriate infrastructure improvements to the most traveled routes in a study area by seeing logical paths that cyclists avoid. A second phase of the project would develop applications allowing riders to express their desired bike routes even if they currently do not cycle because of lack of adequate facilities.
Team: Kari Watkins (Civil Engineering) and Chris Le Dantec (LMC)
2011 Research and Engagement Grants
Each year, GVU provides seed grants, with funding support from IPaT, to research initiatives committed to building on our success in interdisciplinary research and innovation in the human experience of computing. These investments create a path for external funding as our research prospers.
New Media Nollywood
The Nigerian film industry, colloquially known as Nollywood, is the world's most prolific movie maker. The industry produces 40 new movies a week, perhaps five times as many as come from Hollywood, creating one of Africa's most significant and dynamic cultural export. New Media Nollywood week at Georgia Tech will offer a chance for the GVU community to engage with this vibrant visual media, and to help explore and invent it's use of social, interactive and multimedia technologies. We will host more than 20 of Nollywood's top media scholars, producers, directors and film stars. Their visit will be centered around a series of technology deep-dives, where we will collectively investigate new media technologies and the Nigerian film industry. The week will end with a one-day international workshop with the aim of crystallizing a shared vision for Nollywood and new digital technologies. Then stick around for the following week, when we plan to shoot an entire Nollywood style film on the Georgia Tech campus.
Team: Mike Best and Angela Dalle Vacche
Visual Analytics for Innovation Ecosystem Intelligence
Converging business ecosystems are become an increasing reatlity in many different domains - including mobile telecom, future media, biotechnology, healthcare and greentech/energy. The idea of having a "crystal ball" that provides capabilities to explore, make sense, and, perhaps, even provide actionable insight into rapidly changing business ecosystems is enormously attractive to many decision-makers, including technology executives, product strategists and investors. Business ecosystem intelligence includes an understanding of the competitive landscape, identification of innovation opportunities and strategic collaborations, and prediction of possible new product-market fit. We are exploring the design and development of a system that will take a variety of diverse data and document types and will provide the end-user with useful ecosystem intelligence. We take a visual analytics approach, combining computational analysis and text mining techniques with interactive visualizations, in order to create an environment that will allow an analyst to explore relevant information and gain a deeper understanding of converging ecosystem activities, evolution and opportunities.
Team: Rahul Basole and John Stasko
Driving Advances in Computing Education Through Application of Educational Psychology Principles
The aim of this project is to take advances in the learning sciences over the last couple of decades and apply them to computer science education. This is important because there has been an almost two-decade hiatus in systematic research on computer science education and a number of relevant findings can now be applied. For example, we know more about how students learn from examples, how to use multiple media to reduce cognitive load, and how to teach through student's inquiry. This project will focus on creating examples of computer science instruction that are informed by modern learning sciences research. In so doing, we hope to create a kernel for growing a research program and providing a set of papers that connect the computing education research community to new ideas in education, psychology, and learning sciences. Our student audience will be in-service high school teachers who wish to become computer science teachers. New funding in NSF aims to train 8,000 new computer science teachers in the next four years. We will choose a computer science topic from those highlighted as critical in the new “Computer Science: Principles” advanced placement course under development. In this way, we choose a crucial audience and the most relevant content.
Team: Richard Catrambone and Mark Guzdial
Electronic Textiles Swatch Book (eSwatchBook) Workshops
The Electronic Textile Interface Swatch Book (ESwatchBook) Workshops will bring together professionals from both the design and computer science professions for a series of one-day creative endeavors in making wearable technologies. The ESwatchBook will be used in the inspiration and ideation phase of the design process to both foster ideas and act as bridge between disciplines. Observational and survey data will be taken from the workshops to look at the outcome of implementing the ESwatchBook in the design process. Georgia Tech researchers will lead these workshops at top design schools around the country, including Parsons and the Savannah College of Art and Design.
Team: Clint Zeagler and Thad Starner
2010 Innovation Grants
In 2010 GVU invested in three new innovative research projects. Each project in their own way embodies a fresh look on interdisciplinary research, understanding how creativity and computing science can work together to solve problems and create new experiences.
Creativity + Cognition + Computing
The Creativity + Cognition + Computation (CCC) initiative aims to better understand human creative processes and cognition in order to support the development of new tools to assist creative endeavors, such as graphic design and filmmaking, and to build computational systems to generate new artistic creations and approaches to solving problems. The goal of this initiative is to build academic communities to leverage individual research projects into a recognized, unified, and pioneering whole. The group has already been instrumental in bringing the ACM Creativity and Cognition Conference to Atlanta in 2012. The ongoing goal is to identify the various research being done at Georgia Tech which aims to understand creative people, build creative tools, and to develop synergies and collaborative opportunities.
Team: Brian Magerko (IAC, team lead), Carl DiSalvo (IAC), Ellen Do (CoA), Jason Freeman (COA), Ashok Goel (CoC), Nancy Nersessian (CoC), Mark Riedl (CoC)
Games@GT
Georgia Tech is one of the top five universities engaged in computer game research in terms of technology and communications media. Games@GT is an initiative to leverage, expand, and promote Georgia Tech's breadth and depth of faculty expertise in video game research and education by integrating all the gaming-related interdisciplinary research across the Georgia Tech campus.
Team: Mark Reidl (CoC, team lead), Ellen Do (COA), Blair MacIntyre (CoC), Celia Pearce (IAC), Aaron Lanterman (CoE), Brian Magerko (IAC), Ashwin Ram (CoC)
UrbanRemix
The UrbanRemix project was created to explore community-inspired participatory art experiences using locative media captured by mobile phones. The goal is to develop new technology for making art with locative media and explore urban communities' experience in creating art. The computing technology consists of a mobile phone application and a web interface developed by the UrbanRemix team. Using the phones participants in the project become active collectors of location-coded sound and images in their urban environment and use the web interface to browse, remix, and share these sounds on an intuitive map, create spatial compositions of sound, and mix the sounds with music.
People recording city sounds
In June 2010, DiSalvo, Freeman, and graduate student Stephen Garrett took UrbanRemix to the City Centered Festival in San Francisco where they asked neighborhood residents and festival visitors to record sounds from the city's Tenderloin neighborhood. After uploading them to the project's website, Berkeley musician Ken Ueno mixed them into a performance piece.
Later that month, they took their project to Atlanta's Art on the Beltline exhibition, an ongoing event through October designed to entice people to experience this 22-mile loop of rail that aims to revitalize city life.
“Through Urban Remix we want to encourage people to listen to the sounds around them, to discover the hidden music in our neighborhoods, and to collaborate to shape and share that music,” said Freeman.
To experience Urban Remix, visit: http://urbanremix.gatech.edu/ To hear an Urban Remix concert from San Francisco's City Centered Festival, click here
Team: Carl DiSalvo (IAC, team lead), Michael Nitsche (IAC), Jason Freeman (CoA), Aaron Bobick (CoC), Jay Bolter (IAC)


